How to Gamify Learning for Enhanced Learning Outcomes
What is gamified learning and how to gamify learning effectively? Dive into the world of game mechanics like points, leaderboards, and challenges that can turn dull lessons into exciting journeys, improving engagement, motivation, and learning outcomes.
On this page
Imagine a world where every challenge earns you rewards, every task completed is applauded, and you unlock new levels just by pushing your limits. Sounds familiar? That’s the thrill of playing a game.
We’ve all experienced the joy of gaming—chasing points, clearing hurdles, and striving to win. What keeps us hooked? Three things: engagement, interest, and involvement.
When you're truly engaged, you give your best—and that energy is powerful, whether in personal growth or learning. Now, imagine applying that same game-like experience to something traditionally dull—like learning. The impact? Game-changing.
That’s the power of gamification—a proven strategy embraced by businesses, schools, and organizations to make learning and growth more exciting and effective.
With that said, let's understand the nitty-gritty of Game-based Learning and Gamification, challenges in driving engagement to your learning programs, how incentivized Learning can overcome the pain points and more.
What is game-based learning?
Game-based Learning (GBL) is an active learning approach that uses games to teach specific skills and achieve defined outcomes. It makes learning fun and engaging by providing a safe space to apply concepts—like stock trading simulations in economics. GBL is now widely used in corporate training to build skills in areas such as customer service, tech, and teamwork.
What is gamification?
Gamification is the process of incorporating game mechanics or elements into an overall experience to boost enjoyment or engagement. (Source: Mind Research Institute)
Gamification is about adding game elements to non-gaming activities to trigger specific user behaviors. Gamification turns a particular process of learning into a game. It uses gameplay elements & game mechanics to apply in the learning courses to engage and motivate learners.
Interestingly, any activity can be gamified, and it isn’t just limited to learning. From fitness apps to finance platforms, gamified learning strategies are showing up everywhere.
Examples of game mechanics include:
- Points
- Rewards
- Achievement badges
- Progress bars
- Leaderboards
- Levels/quizzes
Interestingly, any activity can be gamified, and it isn’t just limited to learning. That’s why things that you use on a day-to-day basis—from fitness apps to financial apps to your LinkedIn pages—everything is gamified to boost user participation and increase engagement.
Difference between gamification and game-based learning
While Game-Based Learning (GBL) turns the entire learning process into a game, Gamification uses games as a part of the learning process.
Organizations are increasingly adopting gamified learning to boost retention, improve performance, and make content stickier.
The primary difference between GBL (Game-Based Learning) and Gamification is the inclusion of game mechanics in the training content. Since GBL integrates both, the game is actually the training itself. On the other hand, gamification utilizes game elements as rewards to complete training modules.
|
Applying GBL (Game-Based Learning) |
Applying Gamification |
|
In
game-based learning, learners understand new concepts and practice their
skills in a risk-free environment. Progress is directly associated with the
subject’s understanding that’s being taught. |
Gamification integrates engagement tools
with existing content to motivate learners. While adding progress bars or
levels to existing content sounds pretty straightforward, things get complex
when you place the participants on leaderboards (for example) or deliver
points whenever they give correct answers. |
|
GBL is all about making learning fun. It
has a considerable impact on learners’ recall and retention rates. Here,
users are engaged and interested in the subject matter. When there is an
increased engagement rate, it impacts retention as well. |
Gamification is all about driving
engagement. The elements of gamification work on the foundation of a human’s
need to compete, collect and succeed. |
|
GBL gives a learner the liberty to
practice or apply the skills they have learned without any real-world implications.
Users receive feedback to help them know how well they are doing and refine
their skills prior to applying them in the real-world. This is something that
LMS (Learning Management Systems) solve. |
GBL gives learners the liberty to
practice or apply the skills they have learned without any real-world
implications. Users receive feedback to help them know how well they are
doing and refine their skills before using them in the real world. This is something
that LMS (Learning Management Systems) solves. |
|
Some applications include: Policy review Customer service training Company training Staff awareness training Team building |
Some applications include: Product innovation On-boarding L&D program engagement Employee error elimination Collaborative learning |
Challenges with learning programs in different use-cases
The benefits of engaged learning are plenty. Whether it's a school or an organization, everyone prefers enhanced engagement, better completion rates, higher retention, and increased satisfaction.
With various learner engagement advantages—probably, enough to convince—you might wonder why a crucial factor like 'engagement' is so hard to achieve? The reason is that some complex obstacles stand in the way of accomplishing higher learner engagement.
Let’s understand the challenges of learning programs in different use-cases.
1. Challenges corporates face with employees during training programs
When it comes to corporate training programs or L&D programs, attention isn’t enough. Sadly, the majority of L&D leaders face multiple challenges that have immediate fixes, but they fail to implement at the right time.
Here are some common challenges of corporate training programs:
· One-size-fits-all approach: Forcing learners down the same path doesn’t work. Let them choose their training based on interests to meet goals faster.
· Complicated learning software: With remote training, support is limited. A user-friendly LMS with self-help tools, tutorials, and demos makes a big difference.
· Low course completion rates: Flexible training access isn't enough. What’s missing is motivation.
· Lack of engagement: Learning alone isn’t always rewarding. Offering meaningful rewards and gathering feedback boosts engagement and participation.
· Boring or irrelevant rewards: Generic or mismatched rewards (like pet vouchers for non-pet owners) can demotivate. Rewards should be personalized and location-flexible.
· No competitive elements: Without points, ranks, or peer interaction, learners lack drive. Gamification keeps motivation high.
· Delayed rewards: Gratification months later loses impact. Instant recognition through integrated reward systems ensures learners feel appreciated right away.
Instead of dull modules, gamified learning offers learners something to work toward—badges, rankings, or even rewards.
2. Challenges teachers face with students during eLearning programs
Even though technology evolution has enabled many things around us that we haven’t possibly imagined, the sudden shift with e-learning and student behavior after the pandemic hasn’t been as smooth as schools/teachers/trainers/professors/educators wanted it to be. Encountering the pitfalls of online learning can be frustrating for both students and teachers.
Here are some common challenges of educational or e-learning programs:
· Using an outdated LMS: Today’s learners expect intuitive, modern platforms—not clunky, outdated systems. A dull LMS can disengage even the most curious students. An interactive and easy-to-navigate LMS is essential to boost participation and learning outcomes.
· Lack of motivation to learn: Students won’t learn effectively without motivation. Incorporating rewards, tokens, and appreciation for milestones adds the extra push they need to stay engaged and perform better.
· Lack of challenge or competition: Without challenges or healthy competition, learning becomes passive. Challenge-based learning fosters deeper engagement and drives students to push their limits.
· Not using a microlearning approach: Long, dense lessons can overwhelm students. Microlearning—sharing content in small, focused chunks—makes it easier to absorb information and keeps students interested.
3. Challenges learning service providers face with their LMS
Language service providers operate in a competitive and challenging market. Although each business is different, the challenges created by the market are similar.
Here are some challenges faced with by learning service provider:
· Unclear objectives: Launching an LMS without well-defined goals leads to delays, confusion, and unmet expectations. Before implementation, clarify your pain points, audience, and desired outcomes.
· Poor user interaction: If users don’t enjoy using the LMS, engagement drops. Provide clear onboarding and training materials to minimize friction and boost satisfaction.
· Lack of flexibility: An inflexible LMS limits scalability and integration. Third-party plugins help automate tasks, personalize learning, and ensure compliance—missing them is a missed opportunity.
· No personalization: A generic LMS fails to meet diverse learner needs. Personalization—like sending localized rewards or motivating features—is essential for engagement and effectiveness.
· No learner incentives: Without gamified rewards or challenges, learners lack motivation. Incentivized e-learning drives behavior change, but it needs a robust, scalable LMS to handle the complexity.
Gamification in learning
Whether it's employees, customers, trainers, or students, gamification serves as one of the most influential and brilliant strategies to motivate people. Triggering those human desires with gamification can engage and enhance the overall learning experience of the learners.
Let's understand this with a simple example.
Assume that you are given a job to get a group of kids to do two tasks without any forceful actions:
- Task 1: Ask the kids to finish their homework
- Task 2: Ask the kids to read a book
Will they do it? No.
Study time is not entertaining at all. We all have been there as kids ourselves. It's as boring as hell. But let's say that these kids were asked to play games instead of studying. What would be the outcome then? They will be ready to play all night long, sacrificing their favorite meal and a good night's sleep without complaining. Why?
Well, it's because of the joy of experiencing things that are far better and more entertaining than studying. Components like unlocking new game levels and achieving things as they progress are what makes them stay.
Now, let's say you have an option to combine gaming elements with education. What would be the result then? The same kids will be more enthusiastic about reading a book or finishing their homework willfully. That's the hidden potential of gamified learning.
Elements of gamification and how to use them in learning
Rewards, leaderboards, badges, or any other element that can motivate or satisfy a learner are called game elements.
Again, these elements are categorized into two types: Game mechanics and Game dynamics.
1. Game mechanics
Game mechanics are used for gamifying a process (or content in the learning use-case). They help drive user behavior through points, rewards, feedback, and other types of incentives. These are the foundations for any non-gamified entity.
List of game mechanics include:
- Ranks and levels
- Scores and leaderboards
- Badges and trophies
- Individual or team tasks
- Virtual currency
- Challenges & unlocks
- Visualized dashboard
- Avatars and individual profile
2. Game dynamics
Game mechanics have the power to drive the user's motivation, but the drawback is it's only for a while. When things get repetitive users get bored again. And that’s where game dynamics play a vital role. Game dynamics amalgamates the behavior of the user with the game mechanics—helping them to evolve over time and prevent the game from being monotonous.
List of game dynamics include:
- Collaboration
- Competition
- Progress
- Achievements
- Rewards
- Collection
Key principles of gamifying learning
Gamified learning offers numerous benefits, but its success hinges on proper implementation. Since each organization is unique, what works for one may not be successful for another.
The ideal strategy can vary significantly based on individual needs and expectations from the process. Some essential factors to consider when developing a gamification strategy are listed as follows:
- Clear and definite goals: The effectiveness of gamified learning depends on the quality of goal setting and feedback mechanisms, as indicated by a psychological study conducted by Research Gate. To achieve maximum results, expectations should be crystal clear, and feedback should remain consistent. For example, if you implement a point system, employees must fully understand the rules and the significance of earning these points. Any points awarded or withheld should come with a clear explanation as well.
- Progress tracking: It is crucial to establish an easy-to-read, transparent metric for tracking progress. Companies may choose to measure performance through different metrics like badges, points, or leaderboards to infuse a gamified appeal. Additionally, communicating the rewards of each process well in advance ensures employees understand what's at stake and helps maintain motivation.
- Challenge and competition: While fostering healthy competition among employees can make work more engaging and enjoyable, organizations must retain control of the process. Tasks and challenges should be designed with a balance in mind, making them neither too easy, nor too difficult. If competition begins to breed unhealthy rivalries or conflicts, employers must intervene swiftly to mitigate any unpleasant feelings or disputes.
- Collaboration: Promoting teamwork alongside competition can be achieved through regular team-based games. This approach enhances team relations and encourages collaborative problem-solving.
Examples of brands using gamification & GBL (Game-Based Learning) in their applications
Here are some great examples of well-renowned brands across the world that have witnessed success after applying ‘gamification’ in their applications.
1. Nike
In 2010, Nike launched their Nike Run Club, a gamification platform, which went a massive hit among its users. The app was designed to help track and gamify a user’s run time, health levels, the distance covered, and features to compare oneself to their previous recordings or others within the social field.
The pure-play of gamification led to this app’s success. They had attractive leaderboards, rewards, badges, and point systems to drive that engagement they wanted.
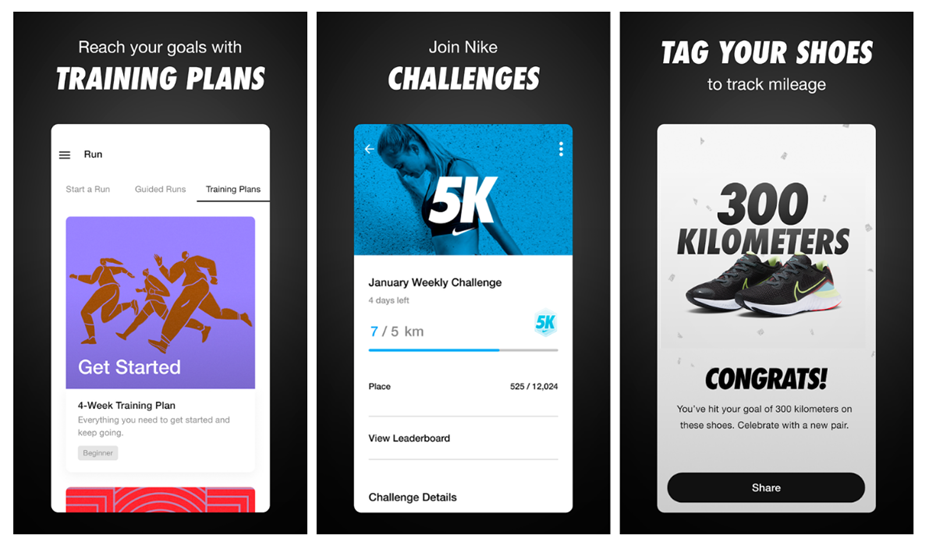
Nike’s Run Club is one of the classic examples of micro-measuring progress and providing live feedback to help runners improve and progress in their day-to-day personal goals.
2. Google Read Along
The recent launch of Google’s Read Along is a perfect example of how a combination of GBL (Game-Based Learning) and Gamification makes learning effective for end-users. The app was launched with an initiative to support families across the world by making ‘learning’ accessible.
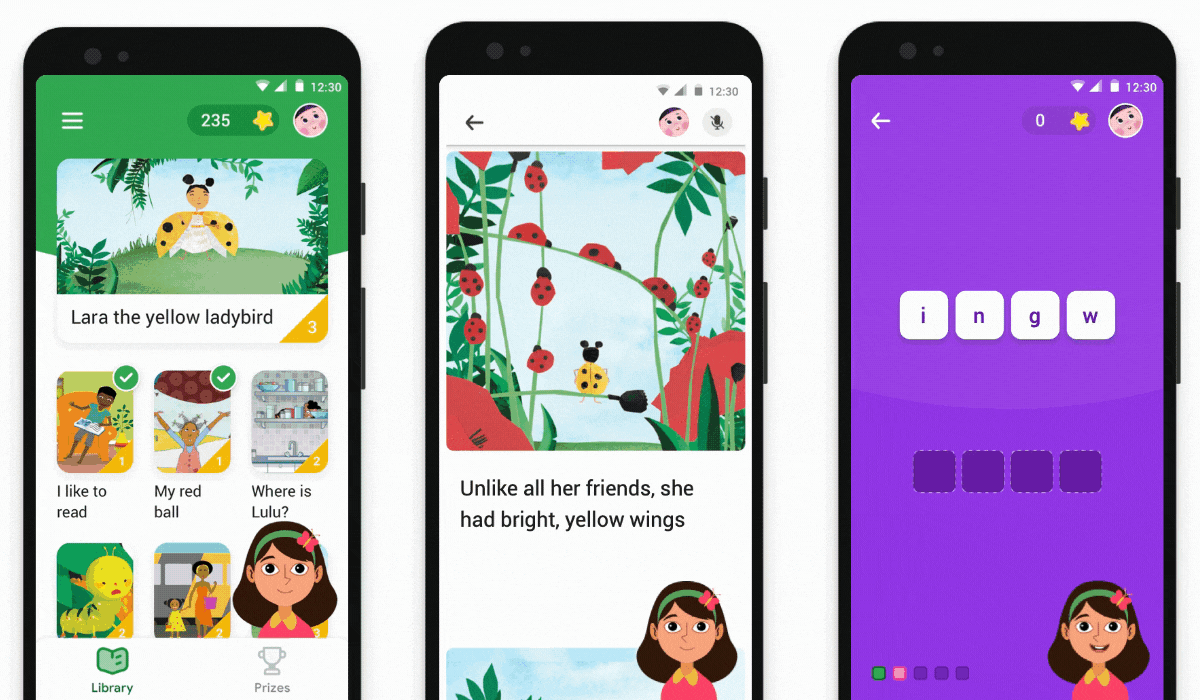
Designed for kids of 5+ years old, the app uses speech recognition technology to develop literacy skills. It is available in 9 languages across 180 countries to make it more accessible. It keeps kids engaged with a diverse collection of exciting stories and interactive games sprinkled in those stories.
They can collect badges and stars as they learn, motivating them to keep reading and playing. It also helps parents to create profiles for various readers, which, when tapped, gives a dashboard showing how each one of them has progressed.
How leveraging LMS integrations can save time and streamline your business
“Seamless integrations” is a term you’ll hear often while searching for the right LMS—and for good reason. A great LMS should effortlessly connect with your existing tools, or you’ll end up with limitations and frustration.
Imagine having an LMS that can’t integrate rewards or lacks CMS connectivity. Sure, you could request custom development—but that’s costly, time-consuming, and complex.
That’s where LMS integrations become essential. They act as the engine that powers smoother operations, enhanced user experience, and smarter decisions.
Why LMS integrations are important:
- Sync effortlessly with third-party tools and APIs for maximum flexibility.
- Enable cross-platform data sharing for better learner insights and training impact.
- Save time and costs by streamlining workflows and reducing manual work.
- Support informed, scalable decisions to grow your learning ecosystem efficiently.
API integrations are the secret weapon behind smarter, faster, and more scalable eLearning and corporate training programs.
By connecting your LMS with third-party tools—like Google Analytics, CRMs, or reward platforms—you unlock time-saving automation, seamless data sharing, and effortless reporting. From auto-enrolling new hires to tracking performance in real-time, APIs help your LMS do more, with less effort.















